 |
Diagnostic Kit for Core Antigen of Hepatitis C Virus (ELISA) |
96 assays per kit
CFDA Certified No.: 20153401894 |
【Product Introduction】
This assay employs the qualitative enzyme immunoassay technique. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an anti-HCVcAg monoclonal antibody. Any HCV core antigen present in samples will bind to the pre-coated specific antibody. Following incubation and wash steps, a Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugated anti-HCVcAg antibody is added and binds to the antigen captured by the first antibody. Unbound HRP-conjugated anti-HCVcAg antibody is removed during a wash step. A substrate solution reactive with HRP is added and a colored product is formed in proportion to the amount of human HCV core antigen present in the sample. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
【Product Feature and Application】
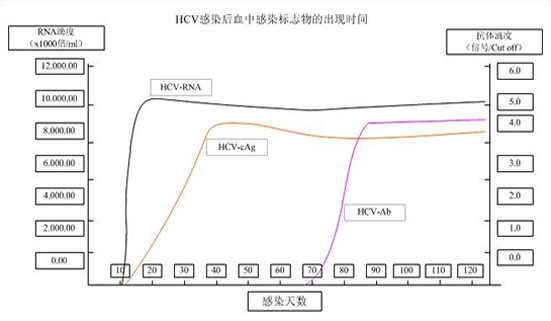
- Shorten the window period of HCV infection. Detect the early phase of HCV infection 70 days to 2 years earlier than the detection of antibodies.
- Applicable in the immunosuppressed population.
- Can distinguish between persons whose past HCV infection has resolved and those who are currently HCV infected.
- Easy to handle, professional instrument needless, suitable for all kinds of hospitals.
【The Interpretation of the Combined Results of HCV-cAg, HCV-Ab and HCV-RNA Test】
HCV-cAg |
HCV-Ab |
HCV-RNA |
Interpretation |
- |
- |
- |
No HCV infection (Report negative if HCV-cAg and HCV RNA keep negative for 2 months) |
- |
+ |
- |
Past HCV infection (Report negative if HCV-cAg and HCV RNA keep negative for 2 months, and past HCV infection has resolved) |
+ |
- |
+ |
Early phase of HCV infection, window period of HCV infection, subject considered to be infectious |
- |
- |
+ |
Early phase of HCV infection, subject considered to be infectious (Keep monitoring all indicators for HCV) |
+ |
- |
- |
Early phase of HCV infection, HCV RNA<103 copies or RNA has been degraded, subject considered to be infectious |
- |
+ |
+ |
Actively infected with HCV, chronic HCV infection, below detectable limit of HCV-cAg, subject considered to be infectious |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Actively infected with HCV, chronic HCV infection, subject considered to be infectious |
+ |
+ |
- |
Actively infected with HCV, hronic HCV infection, HCV RNA<103 copies or RNA has been degraded, subject considered to be infectious |
【How to interpret the results of HCV detection】
For suspected HCV infection, HCV-cAg and HCV-RNA test
should be carried out repeatedly (keep monitoring for 6 months
and carry out the test at least once a month).
【How to diagnose hepatitis C】
1. Both HCV-cAg and HCV-Ab tests results are positive.
2. Both HCV-cAg and HCV-RNA tests results are positive.
3. Both HCV-Ab and HCV-RNA tests results are positive.
4. The results of two consecutive HCV-RNA tests are positive. |
 |
【Latest national policies and regulations related to hepatitis C】
Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hepatitis C |
HCV-cAg test can improve the detection rate of “window period” HCV infection. |
Key points for the prevention and control of hepatitis C by the Ministry of Health |
The primary evidence to diagnose hepatitis C is the detection of HCV-cAg or HCV-RNA. |
Technical Guide for hepatitis C by the national CDC |
The diagnosis of hepatitis C is mainly based on the detection of HCV-cAg or HCV-RNA. |
Standard Technical Procedures for Blood Station (2012) [Department of Medical Administration, MOH (2012): No.1] |
The detection of HCV-cAg has been included in the standard technical procedures. |
|


